Developer Guide
Implementation of Todo Feature
The todo feature implemented using Todo, which extends Task.
Upon receiving an input string that has todo as the first word, the Duke object will instantiate a
Todo object with the fullCommand string, which is the input entered by the user. The Duke
object will then call the getResponse method in the Todo object with the user input arguments:
Finally, the getResponse method will execute the following steps:
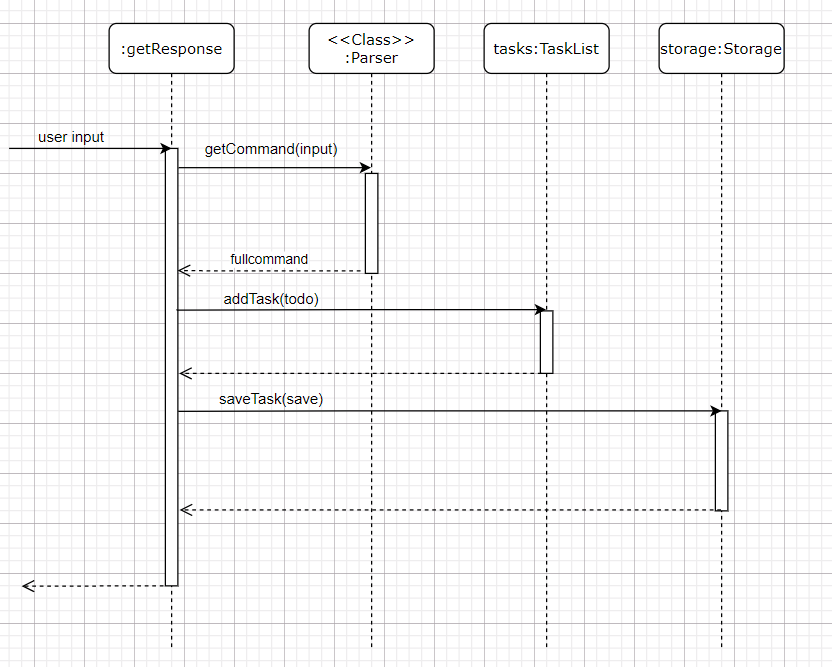
- Calls
Parser#getCommand(fullCommand)to get anTodoobjecttodo; - Calls
tasks#addTask(todo)to addtodototasks; - Calls
storage#saveTasks(tasks)to save all tasks to data file;
The following sequence diagram shows the object interactions when the Duke object calls the getResponse method
of the Todo object:
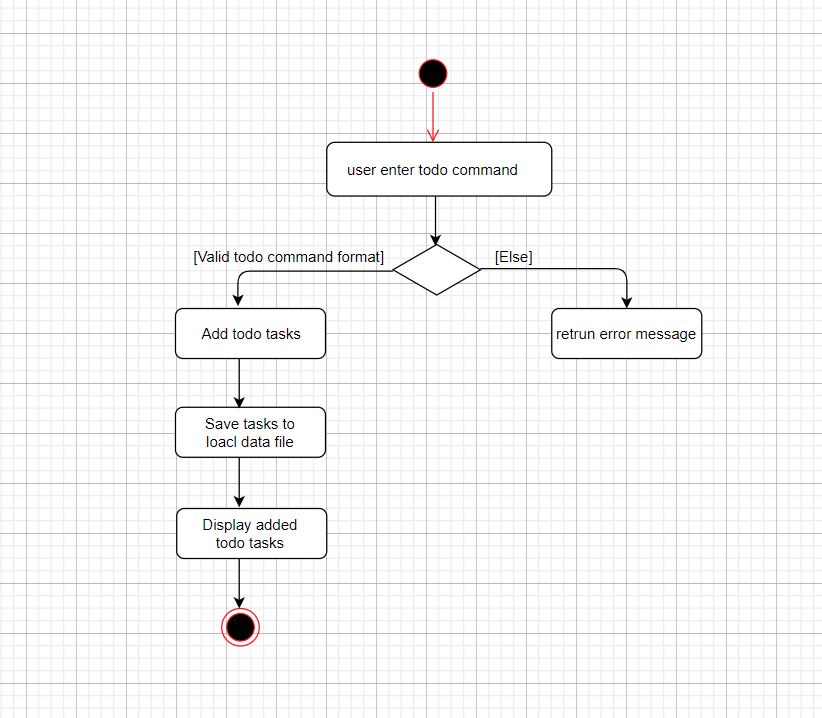
The following activity diagram shows what happens when a user enters a todo command:
User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v0.1 | new user | add a todo task with no deadline | be reminded to do this task |
| v0.1 | new user | add a deadline task with deadline | be reminded to do this task before the deadline |
| v0.1 | new user | add a event task with address | be reminded to do this task at correct address |
| v0.1 | new user | list all tasks | view my assigned tasks |
| v0.2 | user | find tasks | view specific tasks of interest |
| v0.2 | user | mark a task as done | know which of the tasks are completed |
| v0.2 | user | delete a task | remove a task that is no longer needed |
| v0.2 | user | save all tasks | save all tasks to my local folder |
| v0.3 | user | check the use help manual | learn how to use the app quickly and easily |
Non-Functional Requirements
- The application should work on any mainstream OS with Java
11or above installed. - The response time for each command should not exceed
3seconds. - The average typing speed user should be able to enter any one command within
10seconds. - The application GUI should be easily and clearly.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS - Windows 7, Windows 10, Linux, Unix, OS-X